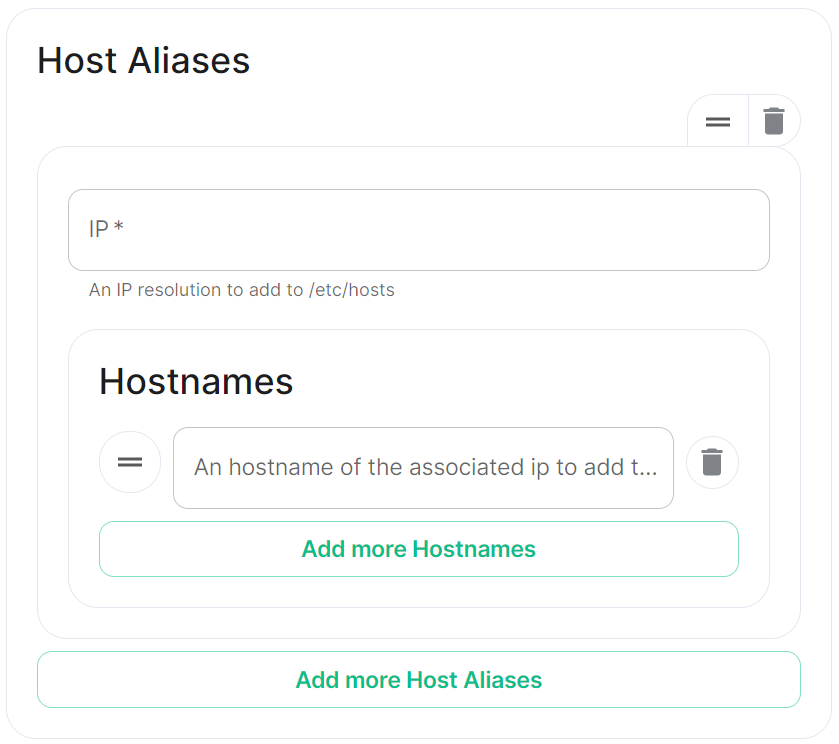
Kubernetes Override Sections
Found in under Advanced in any section where you configure a component of the installer, under the Kubernetes heading. Here you can override Kubernetes configuration for each component.
Common
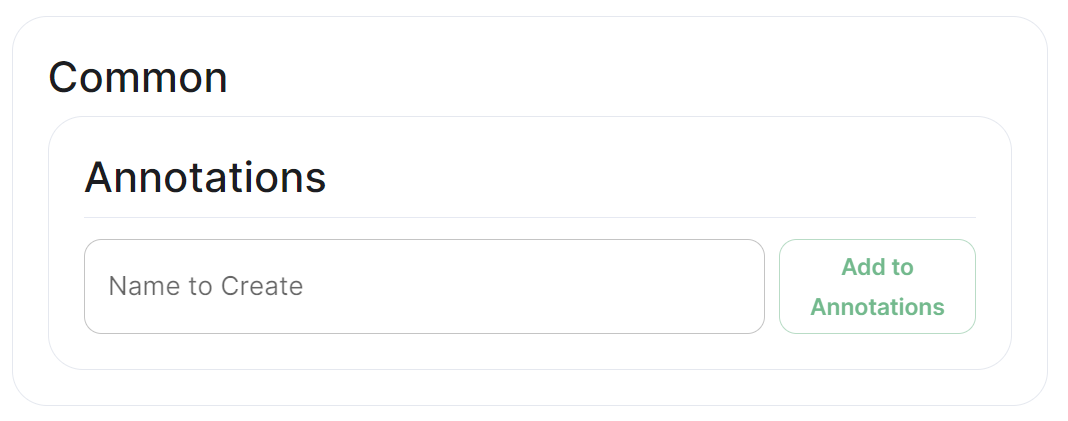
Annotations
In Kubernetes, annotations are key-value pairs associated with Kubernetes objects like pods, services, and nodes. Annotations are meant to be used for non-identifying metadata and are typically used to provide additional information about the objects. Unlike labels, which are used for identification and organization, annotations are more free-form and can contain arbitrary data.
Annotations are often used for various purposes, such as:
-
Documentation.
Providing additional information about a resource that might be useful for administrators or developers. -
Tooling Integration.
Integrating with external tools or automation systems that rely on specific metadata. -
Customisation.
Storing configuration information that affects the behaviour of controllers, operators, or custom tooling. -
Audit Trailing.
Capturing additional information for audit or tracking purposes.
Ingress
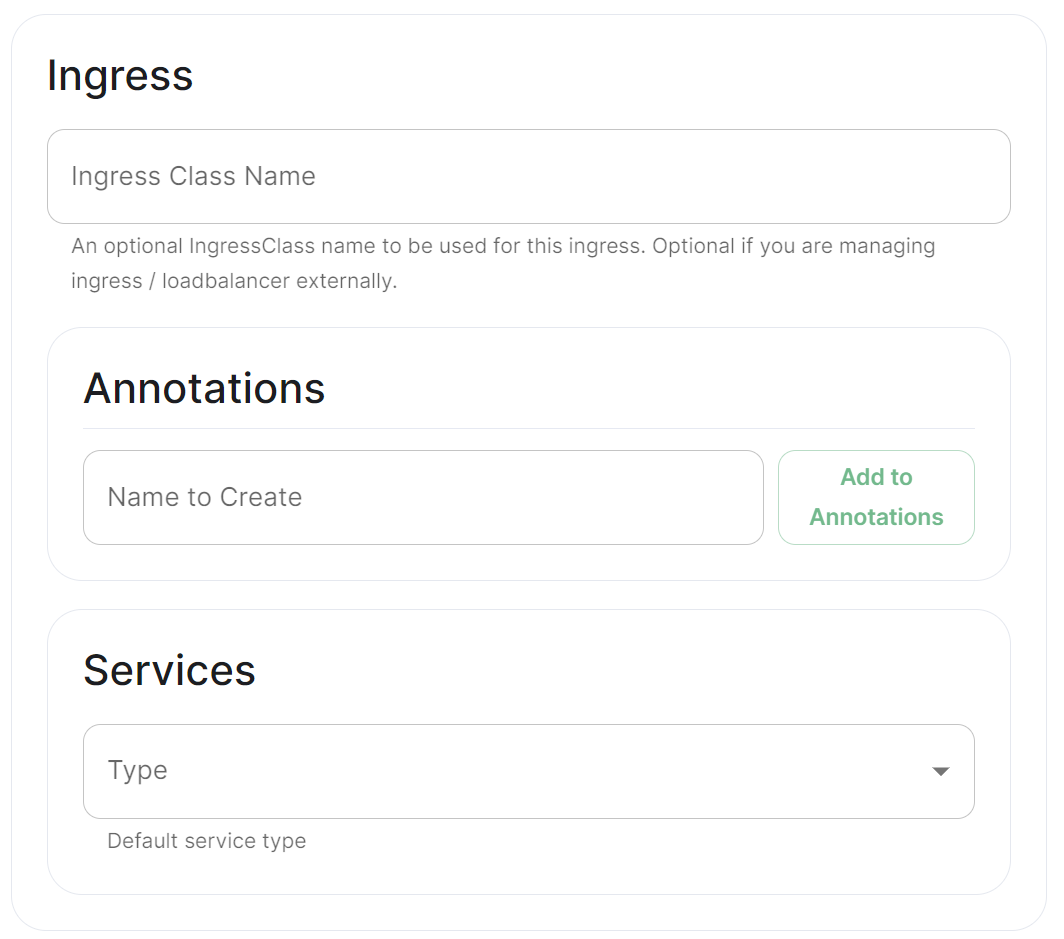 |
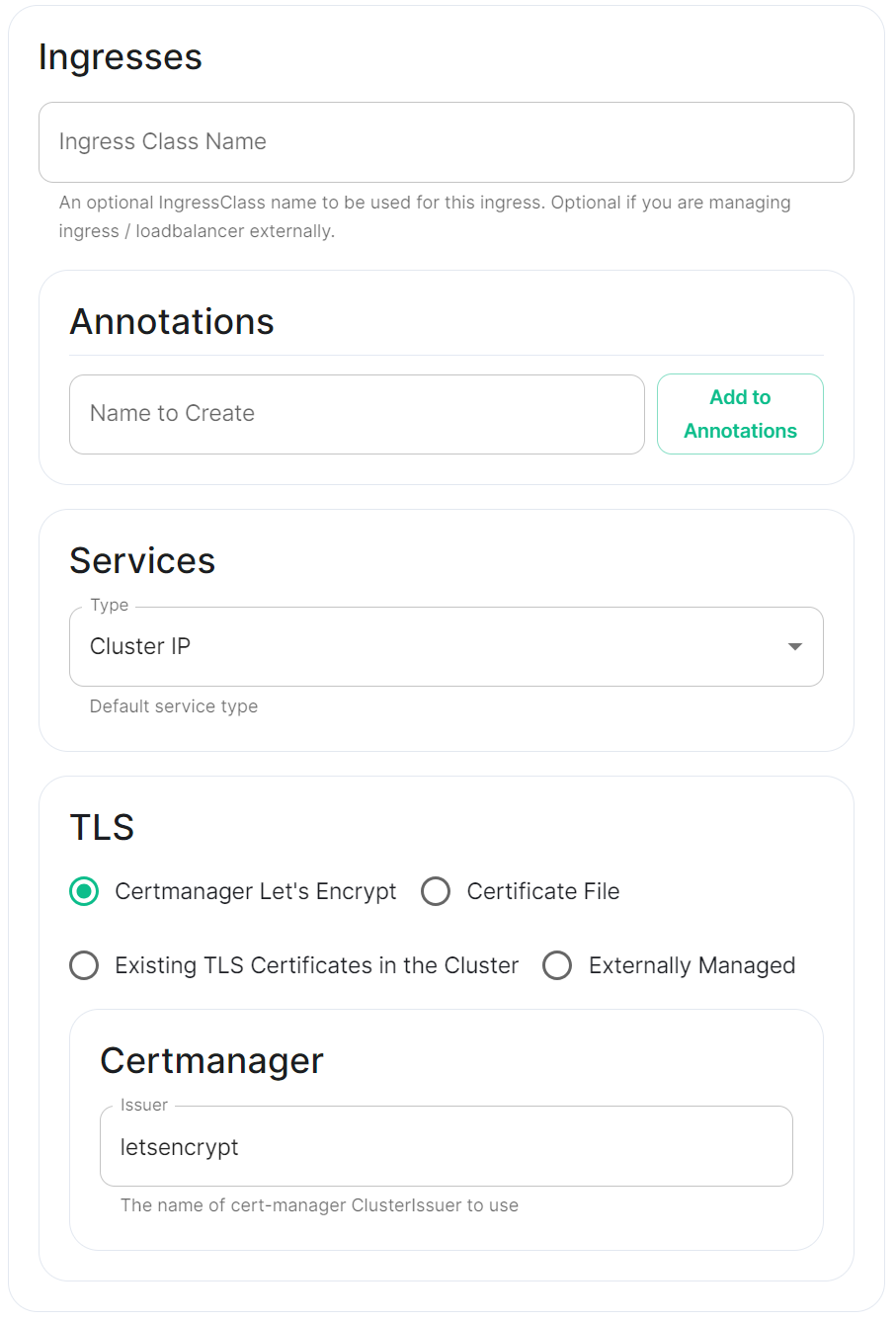 |
Annotations
See explanation of annotations above
Services
Depending on the component you are viewing, you may see Limits and Requests broken out for each sub-component applicable to that component. When configuring Element Web you will only see the Limits and Requests config, for Integrator however, you will see Limits and Requests for each sub-component; Appstore; Integrator; Modular Widgets; and Scalar Web.
Workloads
Annotations
See explanation of annotations above
Resources
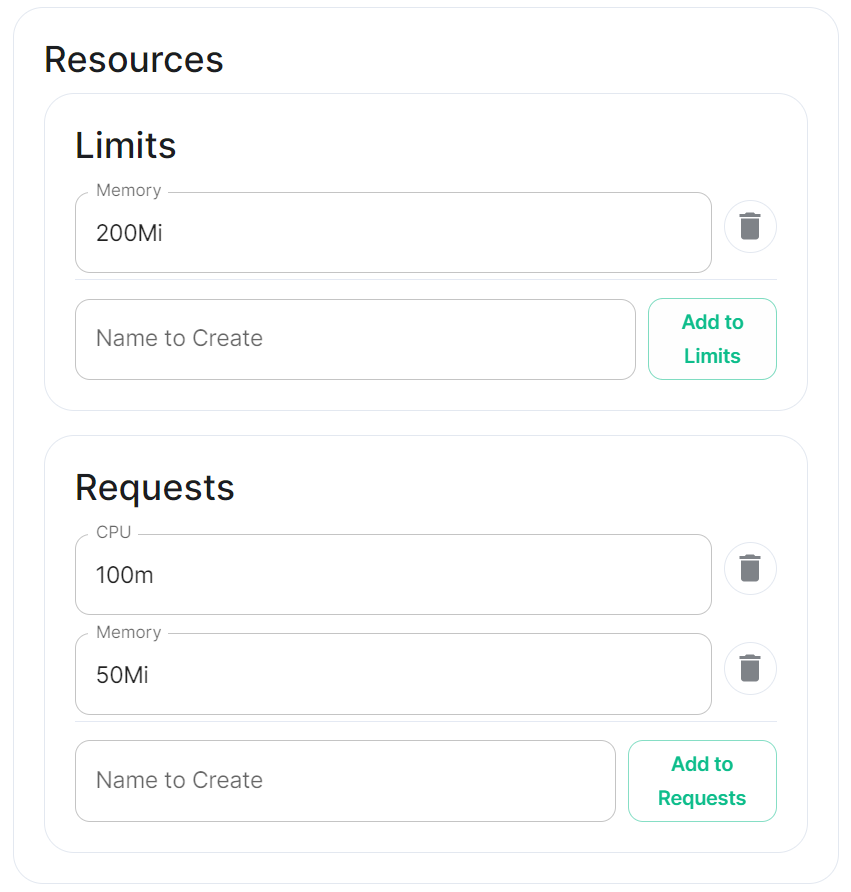 |
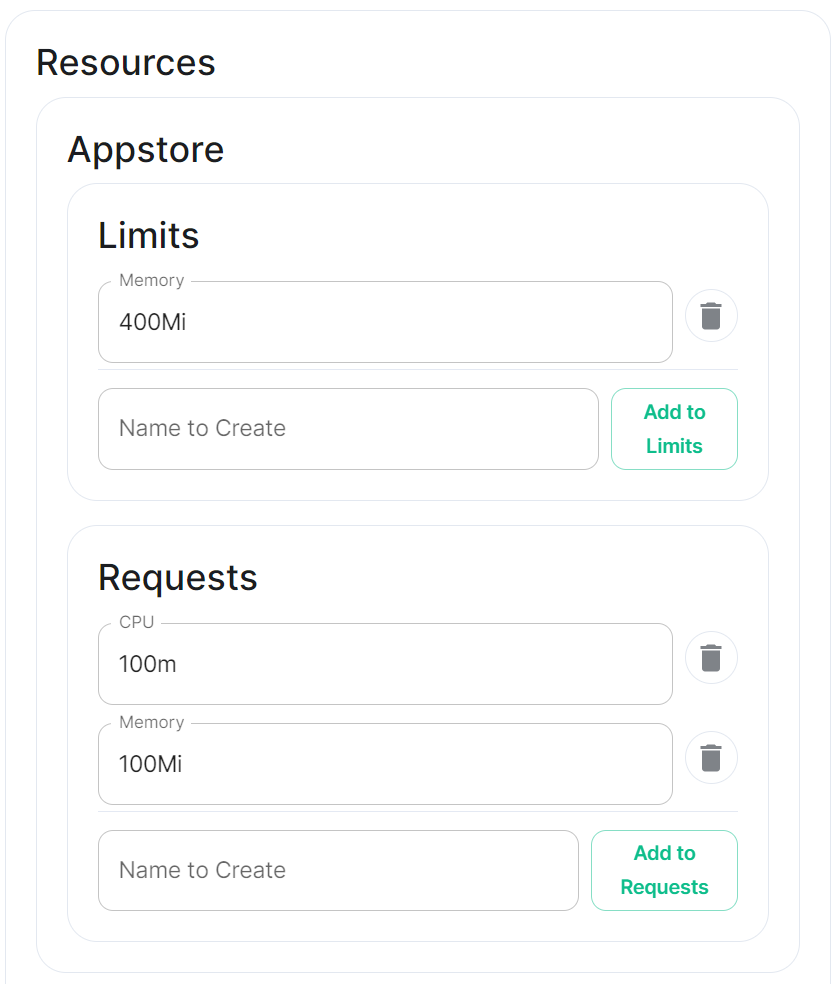 |
Depending on the component you are viewing, you may see Limits and Requests broken out for each sub-component applicable to that component. When configuring Element Web you will only see the Limits and Requests config, for Integrator however, you will see Limits and Requests for each sub-component; Appstore; Integrator; Modular Widgets; and Scalar Web.