Setting up Group Sync with the Installer
What is Group Sync?
Group Sync allows you to use the ACLs from your identity infrastructure in order to set up permissions on Spaces and Rooms in the Element Ecosystem. Please note that the initial version we are providing only supports a single node, non-federated configuration.
Note: This documentation is presently out of date. We will be working to update this in the near future. Until then, if you have questions about setting up group sync in the installer, please file a support ticket or reach out to your Element representative.
Configuring Group Sync
From the Installer's Integrations page, click "Install" under "Group Sync".
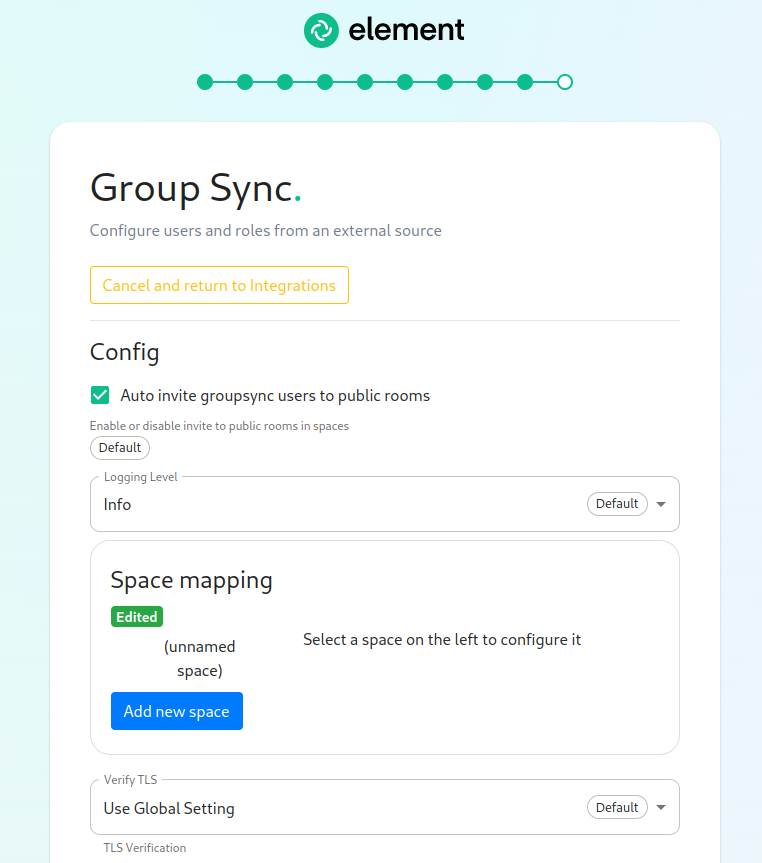
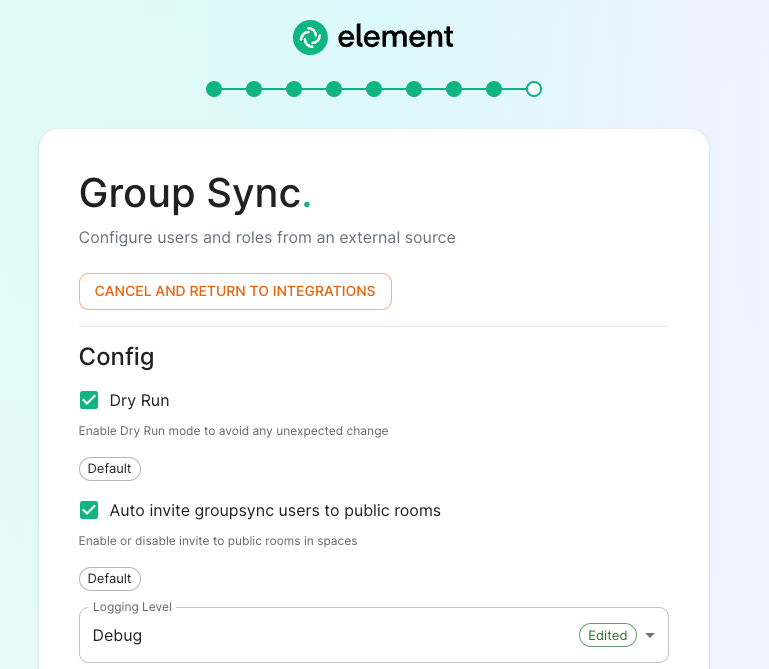
Dry Run checked in combination with Logging Level set to Debug gives you the ability to visualize in the pod's log file what result group sync will produce without effectively creating spaces and potentialy corrupting your database. Otherwise, uncheck Dry Run to create spaces according to your spaces mappings defined in the Space mapping section
Auto invite groupsync users to public room:Configuring the source
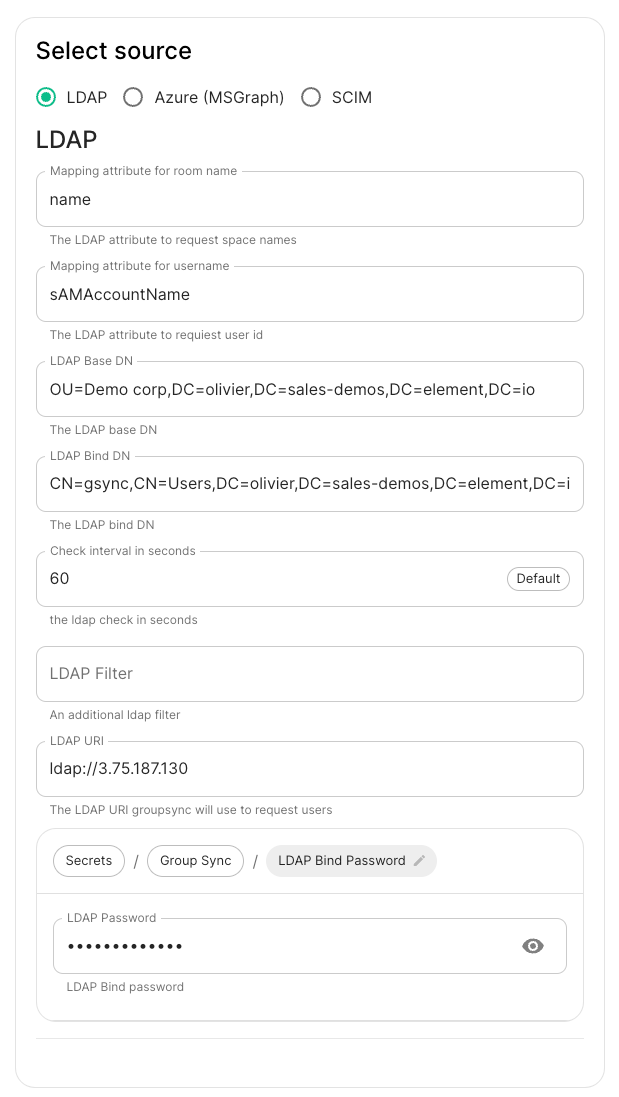
LDAP Servers
- You should create a
ldapLDAP account with readaccess to the OUs containing the usersaccess. - This account should use password
authenticationauthentication.
-
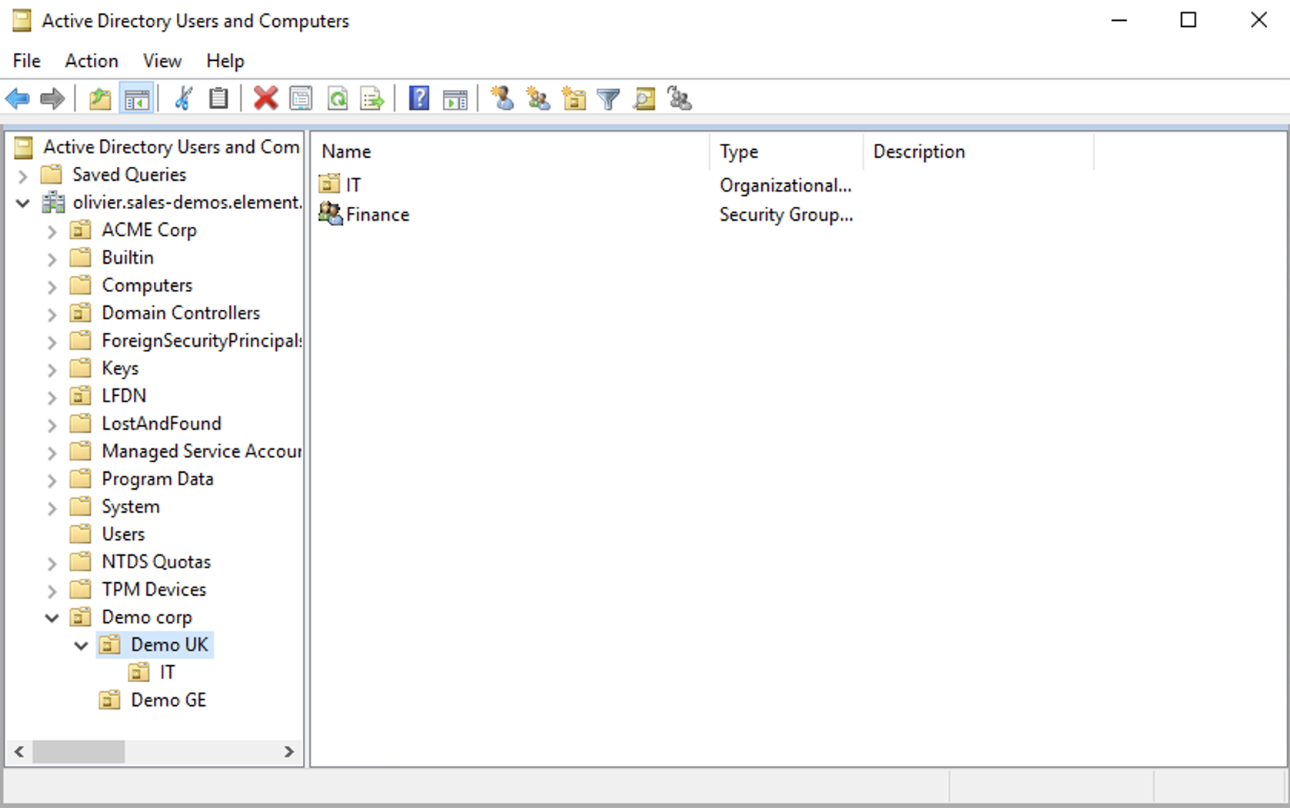
LDAP Base DN: the distinguished name of the root level Org Unit in your LDAP directory. In our example,Demo Corpis our root level, spaces are mapped against Org Units , but you can map a space against any object (groups, security groups,..) belonging to this root level.
The distinguished name can be displayed by selecting View/Advanced Features in the Active Directory console and then, right-clicking on the object, selecting Properties/Attributes Editor.
The DN is OU=Demo corp,DC=olivier,DC=sales-demos,DC=element,DC=io.
-
Mapping attribute for room name: not used but you have to provide a value -
Mapping attribute for username: LDAP attribute likesAMAccountNameused to map the localpart of the mxid against the value of this attribute.If
@bob:my-domain.orgis the mxid,bobis the localpart and groupsync expects to match this value in the LDAP attribute `sAMAccountName. -
LDAP Bind DN: the distinguished name of the LDAP account with read access. -
Check interval in seconds: the frequency Group sync refreshes the space mapping in Element. -
LDAP Filter: an LDAP filter to filter out objects under the LDAP Base DN. -
LDAP URI: the URI of your LDAP server. -
LDAP Bind Password: the password of the LDAP account with read access.
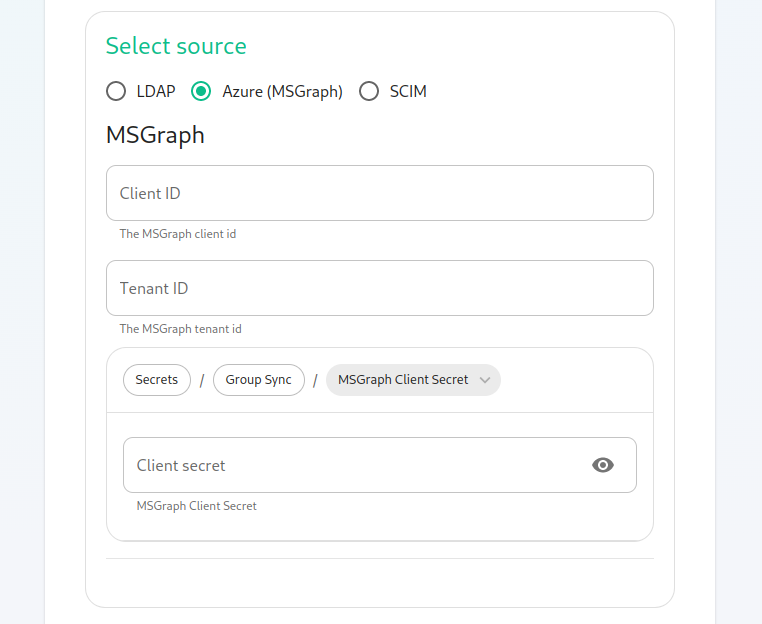
MS Graph (Azure AD)
-
You need to create an
App registration. You'll need theTenant IDof the organization, theApplication (client ID)and a secret generated fromCertificates & secretson the app. -
For the bridge to be able to operate correctly, navigate to API permissions and ensure it has access to Group.Read.All, GroupMember.Read.All and User.Read.All. Ensure that these are Application permissions (rather than Delegated).
-
Remember to grant the admin consent for those.
-
To use MSGraph source, select MSGraph as your source.
-
msgraph_tenant_id: This is the "Tenant ID" from your Azure Active Directory Overview -
msgraph_client_id: Register your app in "App registrations". This will be its "Application (client) ID" -
msgraph_client_secret: Go to "Certificates & secrets", and click on "New client secret". This will be the "Value" of the created secret (not the "Secret ID").
-
Space Mapping
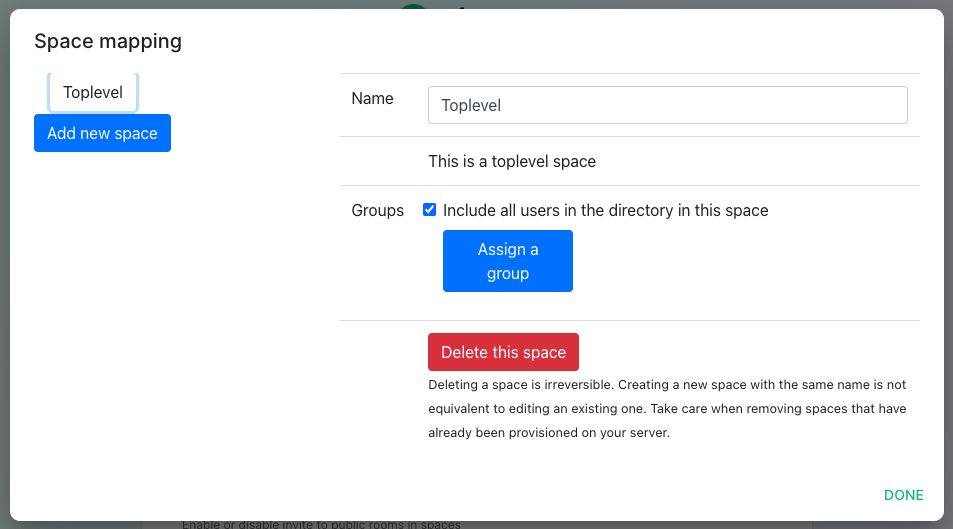
The space mapping mechanism allows us to configure additional spaces that Group Sync will maintain, beyond the ones that ityou createscan bycreate default.manually.
It is optional – the configuration can be skipped but if noyou additionalenable spacesGroup areSync, you have to beedit created.the Space mapping by clicking on the EDIT button and rename the (unnamed space)to something meaningful.
Include all users in the directory in this space: all available users, regardless of group memberships.
Add new space, you can leave the space as a top level space or you can drag and drop this space onto an exisitng space, making this space a sub-space of the existing space.
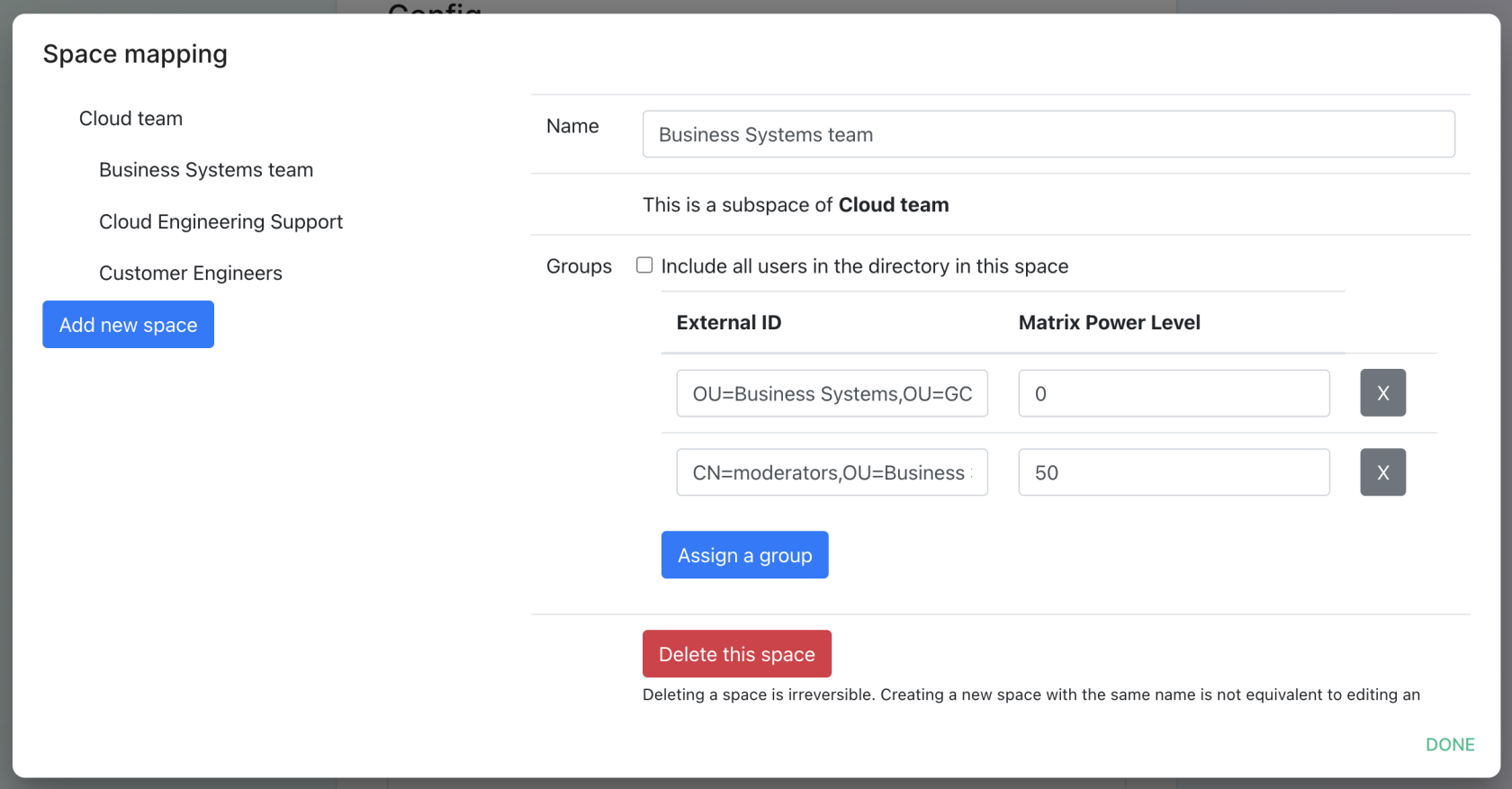
You can then map an external ID (the distinguished name) against a power level. Every user belonging to this external ID is especiallygranted usefulthe whenpower usedlevel withset bridgesin the interface. This external ID that can be any LDAP object like an OrgUnit, a Group or a Security Group
A power level 0 is a default user that can write messages, react to messages.
A power level 50 is a moderator that can creates rooms, delete messages from members.
A power level 100 is an administrator but since GroupSync manages spaces, invitations to the rooms, it does not make sense to map a group against a power level 100.
custom power levels other than LDAP,0 whichand would50 normallyare not createsupported anyyet.
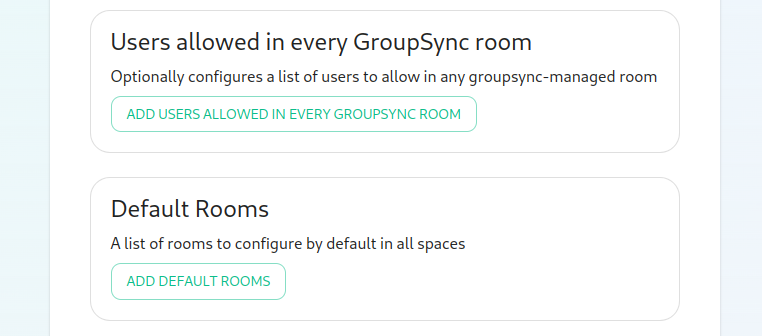
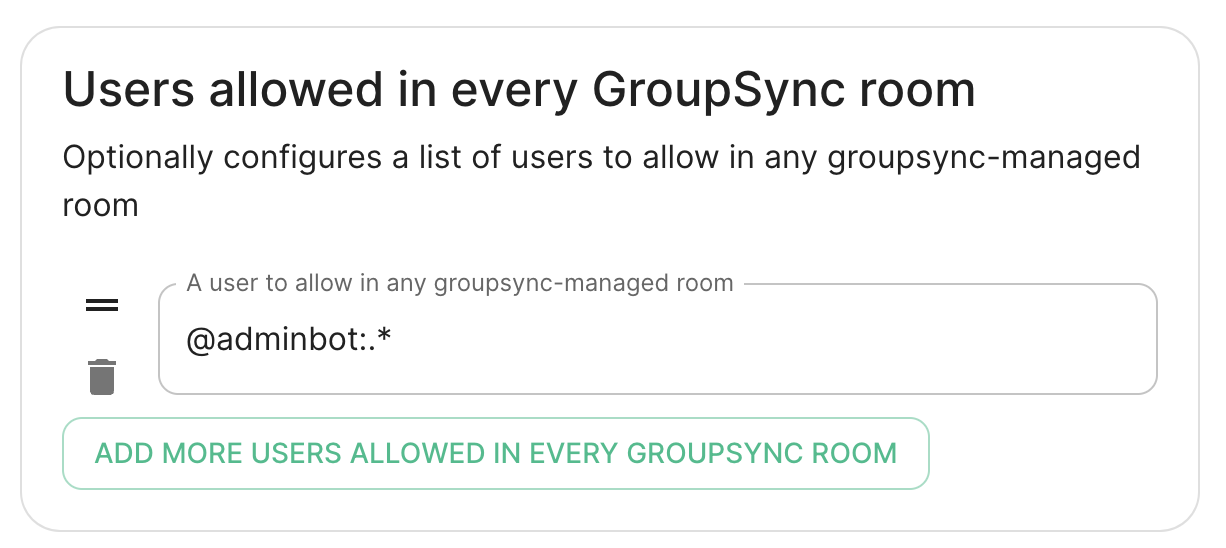
Users otherallowed thanun theevery company-wideGrupSync one.room
A LDAPlist backend,of theuserid spacespatterns createdthat will not get kicked from LDAProoms OrgUnitseven if they don't belong to them according to LDAP.
This is useful for things like auditbot if Audibot has been enabled.
Patterns listed here will be addedwrapped toin the^ and $ before matching.
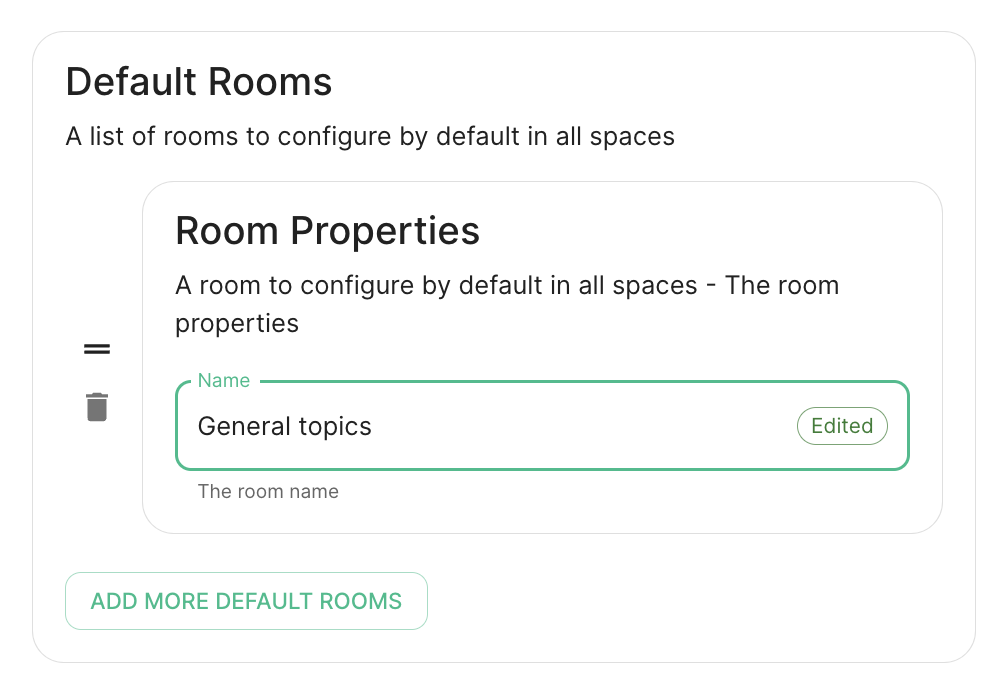
Defaults Rooms
Space mapping also replaces the group power level configuration and group filtering, being a superset of their functionality.
It is recommendedadded to useevery space
mapping in their instead, as they might eventually be deprecated and removed.
The interface provided gives you a graphical way to do this.