Getting Started with the Enterprise Helm Charts
Introduction
This document will walk you through how to get started with our Element Server Suite Helm Charts. These charts are provided to be used in environments which typically deploy applications by helm charts. If you are unfamiliar with helm charts, we'd highly recommend that you start with our Enterprise Installer.
Installing the Helm Chart Repositories
The first step is to start on a machine with helm v3 installed and configured with your kubernetes cluster and pull down the two charts that you will need.
First, let's add the element-updater repository to helm:
helm repo add element-updater https://registry.element.io/helm/element-updater --username
<ems_image_store_username> --password '<ems_image_store_token>'
Replace ems_image_store_username and ems_image_store_token with the values provided to you by Element.
Secondly, let's add the element-operator repository to helm:
helm repo add element-operator https://registry.element.io/helm/element-operator --username <ems_image_store_username> --password '<ems_image_store_token>'
Replace ems_image_store_username and ems_image_store_token with the values provided to you by Element.
Now that we have the repositories configured, we can verify this by:
helm repo list
and should see the following in that output:
NAME URL
element-operator https://registry.element.io/helm/element-operator
element-updater https://registry.element.io/helm/element-updater
Creating namespaces for the element-operator and element-updater
To be able to run the helm charts, they will need a namespace to run in. You can make this whatever you would like, but for the sake of this guide, we will create an element-operator namespace and an element-updater namespace. To do this, please follow this step:
kubectl create ns element-operator
kubectl create ns element-updater
Generating an image-pull-secret
To generate an image-pull-secret to be used by your helm chart deployment, you will need to generate an authentication token using either docker or podman.
To do this with podman, run:
podman login --authfile auth.json gitlab-registry.matrix.org
When prompted for a username, provide your ems_image_store_username. When prompted for a password, provide your ems_image_store_token.
Once this has finished, you will have an auth.json file that has a token which looks similar to:
{
"auths": {
"gitlab-registry.matrix.org": {
"auth": "iNy00NjE2LWIOTFItMWNlYzg5jOWRiOnN5UVlrc3FiRlBtcHhkSDlaOUQ1ZDA2MWI3NDUtY2F5Zm"
}
}
}
Protect this file carefully as it does indeed have your actual login token in it!
Now that we have this file, we need to inject this as a secret into both the element-updater and element-operator namespaces. The commands are as follows:
kubectl create secret -n element-updater generic image-pull-secret --from-file=.dockerconfigjson=auth.json --type=kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson
kubectl create secret -n element-operator generic image-pull-secret --from-file=.dockerconfigjson=auth.json --type=kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson
Installing the helm chart for the element-updater and the element-operator
To install the helm charts and actually deploy the element-updater and the element-operator with their default configurations, simply run:
helm install element-updater element-updater/element-updater --namespace element-updater --set updater.imagePullSecret=image-pull-secret
helm install element-operator element-operator/element-operator --namespace element-operator --set operator.imagePullSecret=image-pull-secret
Now at this point, you should have the following two containers up and running:
[user@helm ~]$ kubectl get pods -n element-updater
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
element-updater-controller-manager-5b4f9cc5d4-9krv6 2/2 Running 6 (8h ago) 2d
[user@helm ~]$ kubectl get pods -n element-operator
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
element-operator-controller-manager-778c8bfbcf-4zzpl 2/2 Running 6 (8h ago) 2d
Generating the ElementDeployment CRD to Deploy Element Server Suite
At this point, you have two options:
-
Use the graphical installer to generate an ElementDeployment CRD for you. (This is the easier and preferred route.) You can find the
ElementDeploymentCRD and the assciated secrets at~/.element-enterpruse-server/configafter running through the installer GUI -
Create a CRD definition on your own starting from this base template:
apiVersion: matrix.element.io/v1alpha1 kind: ElementDeployment metadata: name: <element_deployment_name> namespace: <target namespace> spec: global: k8s: ingresses: ingressClassName: "public" workloads: dockerSecrets: - name: ems-image-store url: gitlab-registry.matrix.org - name: dockerhub url: docker.io - name: element-registry url: registry.element.io storage: storageClassName: "standard" secretName: global config: genericSharedSecretSecretKey: genericSharedSecret domainName: "deployment.tld" components: elementWeb: secretName: external-elementweb-secrets k8s: ingress: tls: mode: certfile certificate: certFileSecretKey: eleweb.tls privateKeySecretKey: eleweb.crt fqdn: element-web.tld synapse: secretName: external-synapse-secrets config: maxMauUsers: 100 media: volume: size: 1 postgresql: host: "<postgresql server>" user: "<user>" database: "<db>" passwordSecretKey: pgpassword sslMode: disable k8s: ingress: fqdn: synapse.tld tls: mode: certfile certificate: certFileSecretKey: synapse.tls privateKeySecretKey: synapse.crt wellKnownDelegation: secretName: external-wellknowndelegation-secrets k8s: ingress: tls: mode: certfile certificate: certFileSecretKey: wellknown.tls privateKeySecretKey: wellknown.crt
If you want to go with point 1, you will need to go get the latest graphical installer. To use this with your helm chart setup, you will need to pick a "Kubernetes Application" install and specify the proper context for the k8s cluster that you wish to deploy the application to. If you do not know what the name of the context is, run:
kubectl config view
and you will see a section similar to:
contexts:
- context:
cluster: microk8s-cluster
user: admin
name: microk8s
current-context: microk8s
In this case, I have one context and its name is microk8s so I would tell the installer to deploy to the microk8s context.
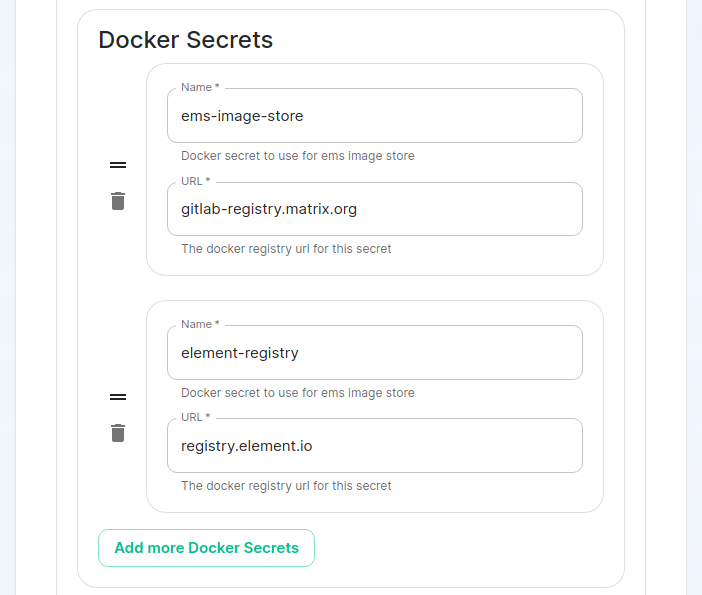
On the cluster page in the installer, under the advanced section, you will want to set up everything you normally would plus add the following docker secrets:
Once you work your way through the installer, set everything up that you wish to have deployed, but do not actually start the installation.
You can close the installer and your CRD is now stored in ~/.element-enterprise-server/config/ as deployment.yml. Your secrets are stored in the same directory as secrets.yml.
Loading secrets into kubernetes in preparation of deployment
N.B. This guide assumes that you are using the element-onprem namespace for deploying Element. You can call it whatever you want and if it doesn't exist yet, you can create it with: kubectl create ns element-onprem.
Now we need to load secrets into kubernetes so that the deployment can access them. If you built your own CRD from scratch, you will need to follow our Element Deployment CRD documentation.
If you went with the installer, you can simply run the following commands:
kubectl create secret -n element-onprem generic ems-image-store --from-file=.d
ockerconfigjson=auth.json --type=kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson
kubectl create secret -n element-onprem generic element-registry --from-file=.d
ockerconfigjson=auth.json --type=kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson
kubectl apply -f ~/.element-enterprise-server/config/secrets.yml -n element-onprem
At this point, you should have a host of secrets loaded into the element-onprem namespace so that kubectl get secrets -n element-onprem generates output similar to:
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
element-web Opaque 2 2d1h
global Opaque 2 2d1h
integrator Opaque 3 2d1h
synapse Opaque 7 2d1h
synapse-admin Opaque 2 2d1h
well-known-delegation Opaque 2 2d1h
ems-image-store kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson 1 2d1h
element-registry kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson 1 2d1h
first-element-deployment-element-tls-secret kubernetes.io/tls 2 2d1h
first-element-deployment-integrator-secrets Opaque 4 2d1h
first-element-deployment-integrator-tls-secret kubernetes.io/tls 2 2d1h
first-element-deployment-synapse-secrets Opaque 6 2d1h
first-element-deployment-synapse-tls-secret kubernetes.io/tls 2 2d1h
first-element-deployment-synapseadminui-secrets Opaque 1 2d1h
first-element-deployment-synapseadminui-tls-secret kubernetes.io/tls 2 2d1h
first-element-deployment-synapse-ca Opaque 1 2d1h
first-element-deployment-wellknowndelegation-tls-secret kubernetes.io/tls 2 2d1h
Deploying the actual CRD
At this point, we are ready to deploy the ElementDeployment CRD into our cluster with the following command:
kubectl apply -f ~/.element-enterprise-server/config/deployment.yml -n element-onprem
To check on the progress of the deployment, you will first watch the logs of the updater:
kubectl logs -f -n element-updater element-updater-controller-manager-<rest of pod name>
You will have to tab complete to get the correct hash for the element-updater-controller-manager pod name.
Once the updater is no longer pushing out new logs, you can track progress with the operator or by watching pods come up in the element-onprem namespace.
Operator status:
kubectl logs -f -n element-operator element-operator element-operator-controller-manager-<rest of pod name>
Watching pods come up in the element-onprem namespace:
watch kubectl get pods -n element-onprem
Updating the helm charts and the underlying deployment
To update the helm charts, you will need to run:
helm repo update
helm uninstall -n element-updater element-updater
helm uninstall -n element-operator element-operator
At this point, you will want to get the newest installer and run it. If you have no changes to make to your config, simply click next to go through the pages. Once you have gotten to the deployment point, close the installer and this will give you an updated CRD if necessary.
If you make any changes to secrets, then you will need to redeploy the secrets.yml following the instructions found earlier in this document.
Now, we can install the newest versions of element-updater and element-operator:
helm install element-updater element-updater/element-updater --namespace element
-updater
helm install element-operator element-operator/element-operator --namespace element
-operator
And then kick off a new deployment of the CRD by doing:
kubectl apply -f ~/.element-enterprise-server/config/deployment.yml -n element-onprem
At this point, you will be running an updated deployment based off of the latest helm charts.