# EMS Server With Custom Domain
For this guide, I will be using the domain
element.io. I will set up EMS so that the
Matrix usernames becomes `@someone:element.io`, and the Element client will be at
https://chat.element.io/
From the guide at [Get Your Own EMS Server](get-your-own-ems-server), I will be replacing the EMS hostname
`ems-demo-staging.ems.host` with `element.ems.host`
Custom domains are only supported with Element Enterprise Cloud plans.
## Prerequisites
- You own and control the domain you want to use
- If you do not have a website on the domain you want to use with your EMS server:
- You can create a CNAME DNS record for the domain. Some providers call this ALIAS or CNAME Flattening when used on
the root of the domain (domain root = `yourdomain.com`, not `something.yourdomain.com`)
- If you have a website on the domain you want to use with your EMS server:
- Your website has HTTPS enabled using a valid certificate issued by a commonly recognized provider. For example,
Comodo or LetsEncrypt.
- You can serve plain-text JSON files at these exact paths
- `https://yourdomain.com/.well-known/matrix/client`
- `https://yourdomain.com/.well-known/matrix/server`
- Note that these files do not and cannot have a file extension
- You can add the header `Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *` to the client file on the web server
## See also
- [FAQ: Can I use a subdomain instead of the root domain with my EMS server?](https://ems-docs.element.io/link/6#bkmrk-can-i-use-a-subdomai)
- [FAQ: Can I use EMS-hosted well-knowns with the root of my domain?](https://ems-docs.element.io/link/6#bkmrk-can-i-use-ems-hosted)
## Setup
Some providers for DNS and website hosting providers need special configuration. See
[Provider specific instructions](#bkmrk-provider-specific-in) at the bottom for known solutions.
1. Follow steps 1 - 10 from [Get Your Own EMS Server](get-your-own-ems-server)
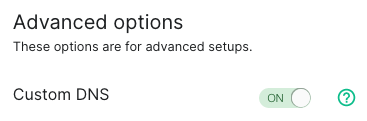
2. On step 10 from [Get Your Own EMS Server](get-your-own-ems-server), turn ON `Custom DNS`
[](https://ems-docs.element.io/uploads/images/gallery/2023-12/image-1702383058866-07-59-am.png)
3. In the `Custom Homeserver domain` field, enter `element.io`
[](https://ems-docs.element.io/uploads/images/gallery/2022-08/image-1659627256442-57-31-pm.png)
4. Create two files on your website according to the instructions given.
The path cannot be changed, but up to 30 redirects are supported.
While not required, you should add the header `Content-Type application/json` to both files.
1. `https://element.io/.well-known/matrix/server`
[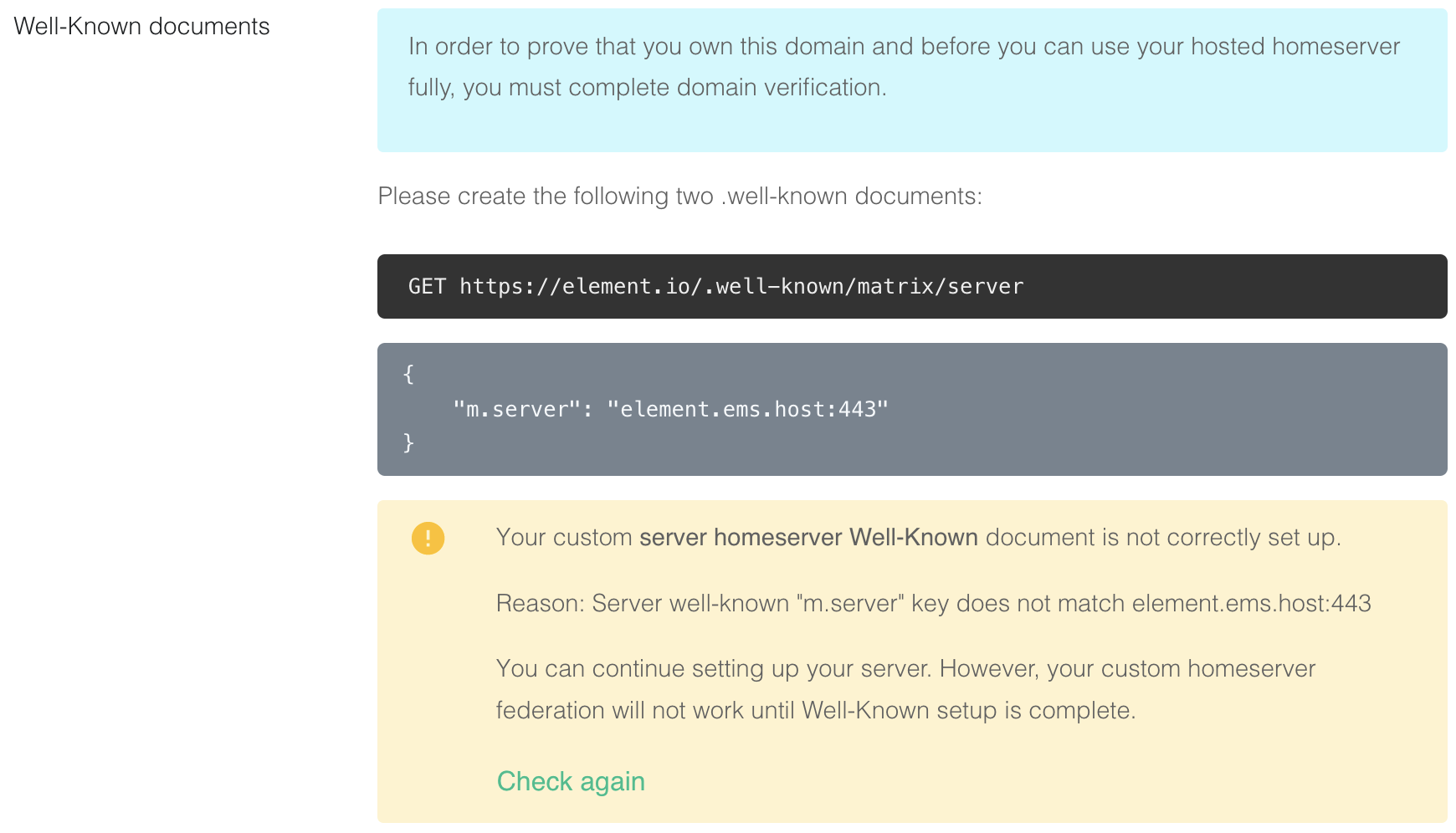](https://ems-docs.element.io/uploads/images/gallery/2022-08/image-1659627292963-32-20-pm.png)
```json
{
"m.server": "element.ems.host:443"
}
```
2. `https://element.io/.well-known/matrix/client`
[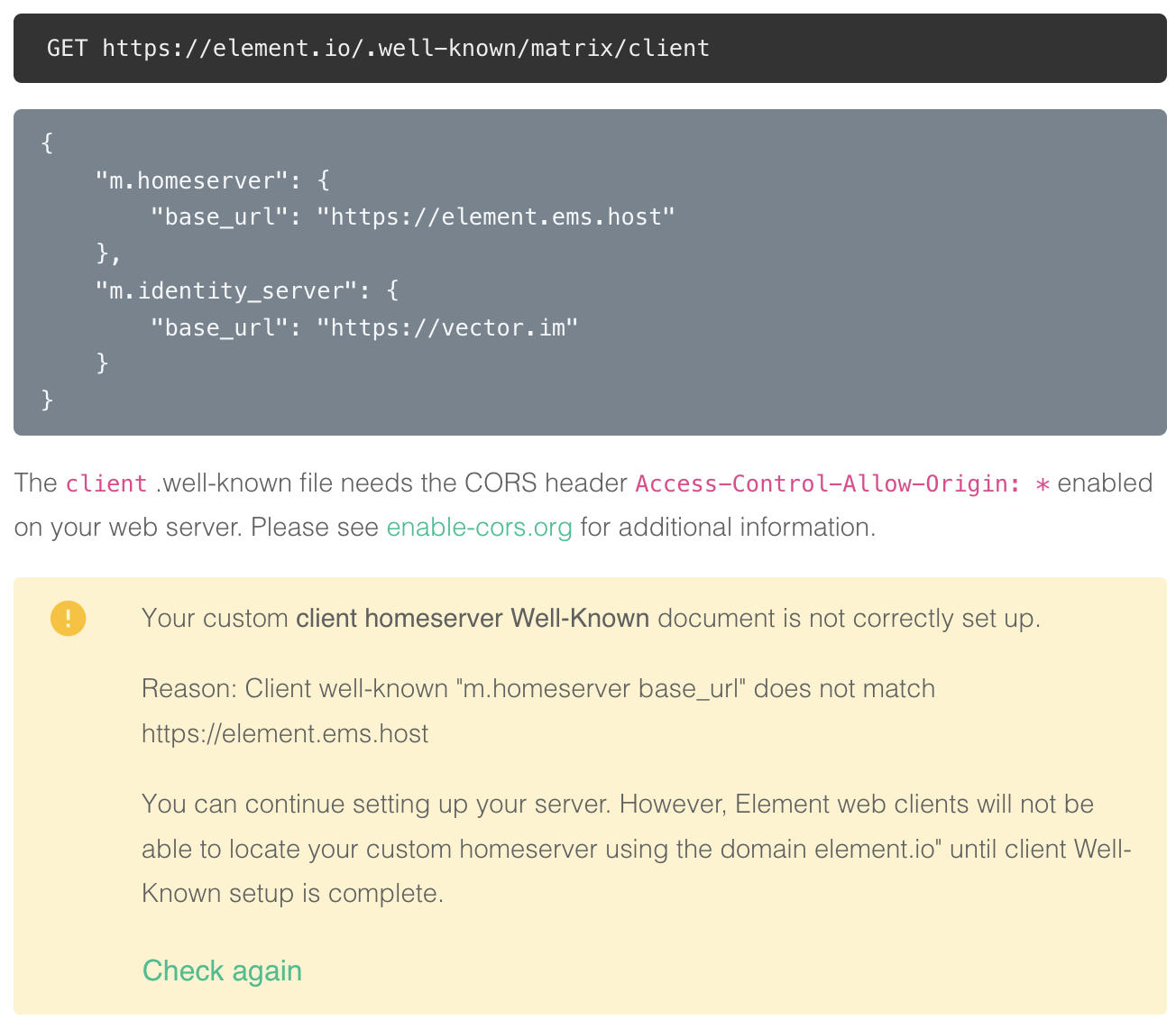](https://ems-docs.element.io/uploads/images/gallery/2022-08/image-1659627321046-32-38-pm.png)
You need to enable the CORS header `Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *` on the web server for this file. See
https://enable-cors.org/ for
instructions on how to do this. If you are using redicrects, the CORS headers must be set on all steps/hops.
```json
{
"m.homeserver": {
"base_url": "https://element.ems.host"
},
"m.identity_server": {
"base_url": "https://vector.im"
},
"org.matrix.msc4143.rtc_foci": [
{
"type": "livekit",
"livekit_service_url": "https://jwt.call.element.io"
}
]
}
```
Optional Nginx-specific configuration
If your web server is running Nginx, you can set this in the Nginx config instead of creating actual files.
```plaintext
server {
server_name element.io
...
# Matrix well-known files
location /.well-known/matrix/client {
return 200 '{"m.homeserver":{"base_url":"https://element.ems.host"},"m.identity_server":{"base_url":"https://vector.im"},"org.matrix.msc4143.rtc_foci":[{"type":"livekit","livekit_service_url":"https://jwt.call.element.io"}]}';
add_header Content-Type application/json;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' '*';
}
location /.well-known/matrix/server {
return 200 '{"m.server": "element.ems.host:443"}';
add_header Content-Type application/json;
}
}
```
5. Click `Check again` to verify that your `.well-known` files are configured correctly
[](https://ems-docs.element.io/uploads/images/gallery/2022-08/image-1659627418181-36-42-pm.png)
You can also verify your `.well-known` files from the command line
Note the lines `access-control-allow-origin: *` and `content-type: application/json`
1. On Mac or Linux, using the `terminal`
```bash
$ curl -i https://element.io/.well-known/matrix/client
HTTP/2 200
date: Fri, 31 Jul 2020 09:11:21 GMT
content-type: application/json
content-length: 129
set-cookie: __cfduid=x...; expires=Sun, 30-Aug-20 09:11:21 GMT; path=/; domain=.element.io; HttpOnly; SameSite=Lax
access-control-allow-origin: *
cf-cache-status: DYNAMIC
cf-request-id: 0...
expect-ct: max-age=604800, report-uri="https://report-uri.cloudflare.com/cdn-cgi/beacon/expect-ct"
server: cloudflare
cf-ray: 5...
{
"m.homeserver": {
"base_url": "https://element.ems.host"
},
"m.identity_server": {
"base_url": "https://vector.im"
},
"org.matrix.msc4143.rtc_foci": [
{
"type": "livekit",
"livekit_service_url": "https://jwt.call.element.io"
}
]
}
$ curl -i https://element.io/.well-known/matrix/server
HTTP/2 200
date: Fri, 31 Jul 2020 09:11:25 GMT
content-type: application/json
content-length: 52
set-cookie: __cfduid=x...; expires=Sun, 30-Aug-20 09:11:25 GMT; path=/; domain=.element.io; HttpOnly; SameSite=Lax
access-control-allow-origin: *
cf-cache-status: DYNAMIC
cf-request-id: 0...
expect-ct: max-age=604800, report-uri="https://report-uri.cloudflare.com/cdn-cgi/beacon/expect-ct"
server: cloudflare
cf-ray: 5...
{
"m.server": "element.ems.host:443"
}
```
2. On Windows, using `PowerShell`
```powershell
PS C:\Users\twilight> Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https://element.io/.well-known/matrix/client
StatusCode : 200
StatusDescription : OK
Content : {
"m.homeserver": {
"base_url": "https://element.ems.host"
},
"m.identity_server": {
"base_url": "https://vector.im"
},
"org.matrix.msc4143.rtc_foci": [
{
"type": "livekit",
"livekit_service_url": "https://jwt.call.element.io"
}
]
}
RawContent : HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Connection: keep-alive
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
CF-Cache-Status: DYNAMIC
cf-request-id: 0...
Expect-CT: max-age=604800, report-uri="https://repor...
Forms : {}
Headers : {[Connection, keep-alive], [Access-Control-Allow-Origin, *], [CF-Cache-Status, DYNAMIC], [cf-request-id, 0...]...}
Images : {}
InputFields : {}
Links : {}
ParsedHtml : System.__ComObject
RawContentLength : 129
PS C:\Users\twilight> Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https://element.io/.well-known/matrix/server
StatusCode : 200
StatusDescription : OK
Content : {
"m.server": "element.ems.host:443"
}
RawContent : HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Connection: keep-alive
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
CF-Cache-Status: DYNAMIC
cf-request-id: 0...
Expect-CT: max-age=604800, report-uri="https://repor...
Forms : {}
Headers : {[Connection, keep-alive], [Access-Control-Allow-Origin, *], [CF-Cache-Status, DYNAMIC], [cf-request-id, 0...]...}
Images : {}
InputFields : {}
Links : {}
ParsedHtml : System.__ComObject
RawContentLength : 52
```
6. You can continue without the `.well-known` files in place, but your server will have limited functionality until this is fixed
7. In the `Custom Client domain` field, enter `chat.element.io`. This can be any domain, except the same as `Custom Homeserver domain`
[](https://ems-docs.element.io/uploads/images/gallery/2022-08/image-1659627867813-44-13-pm.png)
8. Create a CNAME DNS record with your DNS provider according to the instructions given
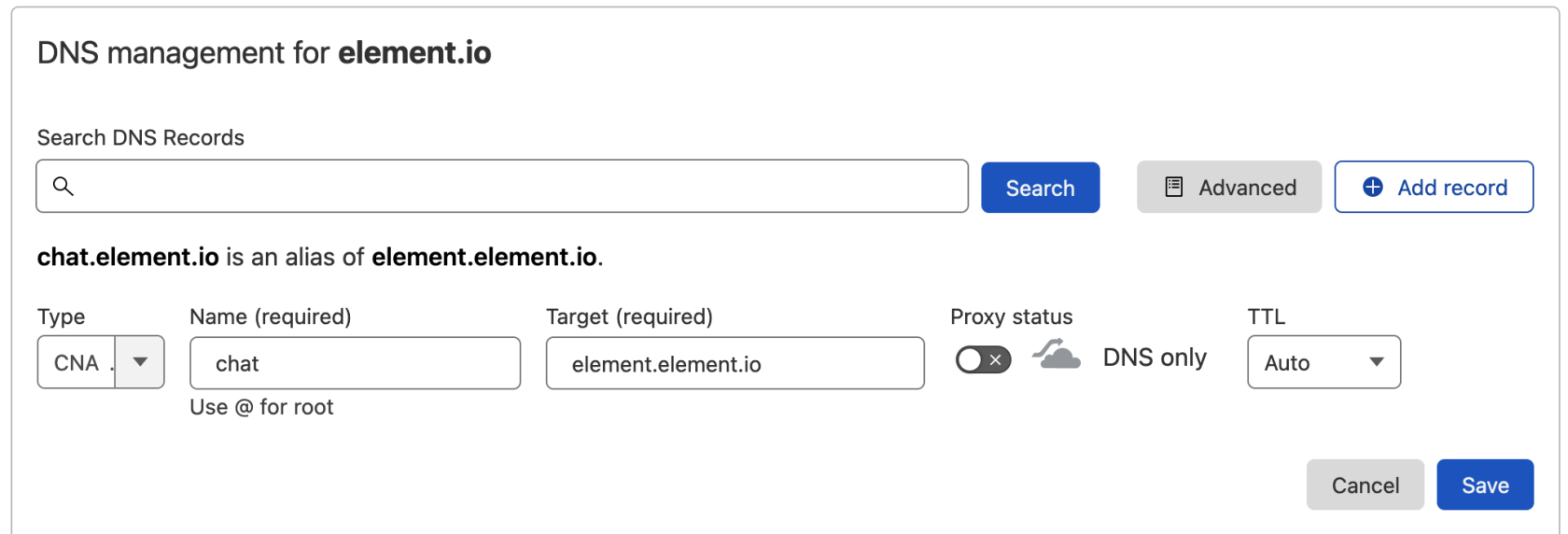
`chat.element.io. CNAME element.element.io.`
[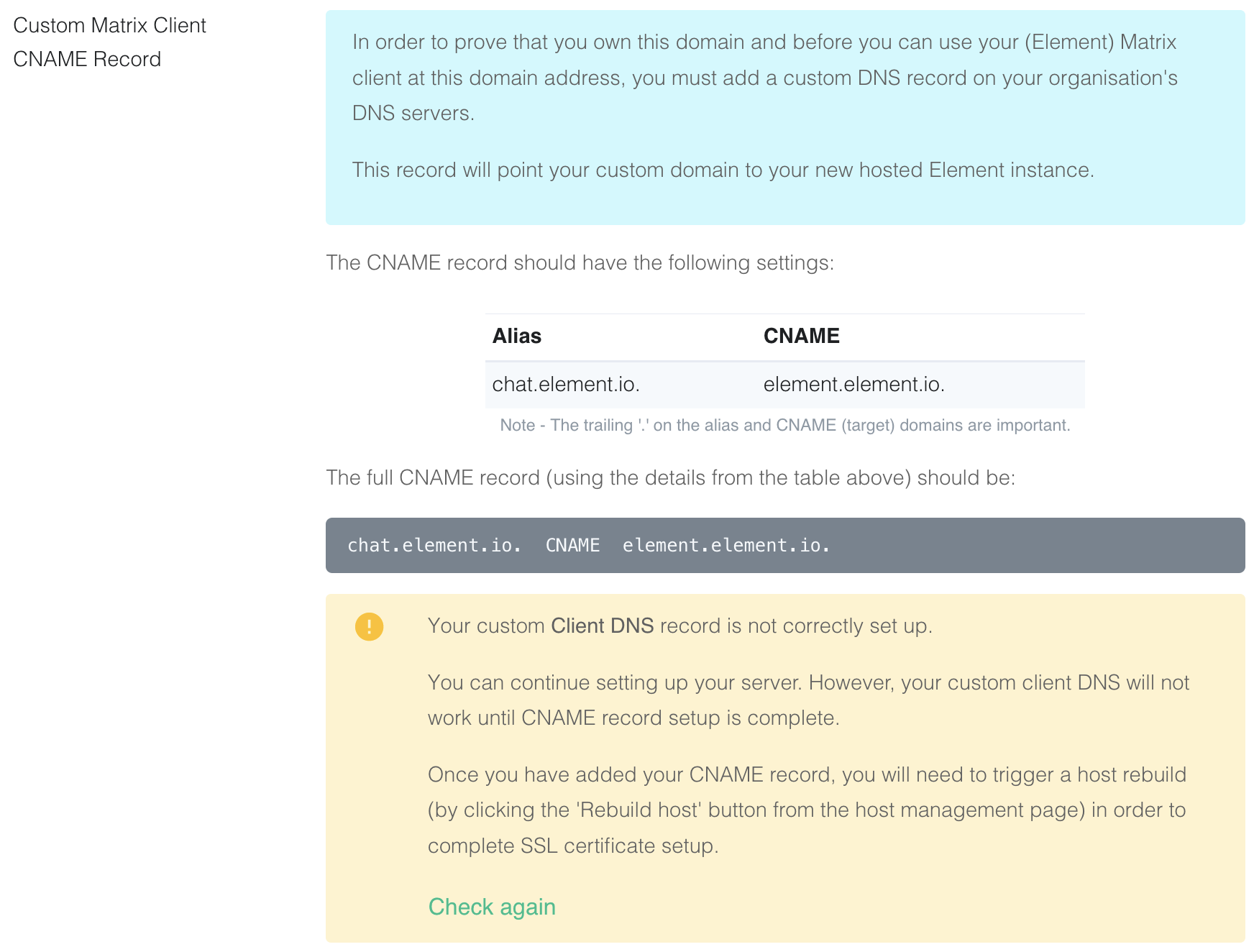](https://ems-docs.element.io/uploads/images/gallery/2022-08/image-1659627663519-40-24-pm.png)
9. This shows how this is done with Cloudflare DNS. Depending on your DNS provider, this might be different. Consult the
documentation for your provider. Note that Proxy must be turned off with Cloudflare.
[](https://ems-docs.element.io/uploads/images/gallery/2022-08/image-1659628294089-50-07-pm.png)
10. Back on EMS, click `Check again`. Note that sometimes it might take a while for your new DNS record to propagate.
You can continue, but functionality will be limited. Check back with the Hosts tab on
https://ems.element.io/user/hosting
and click `Rebuild Host` once the DNS record is in place.
[](https://ems-docs.element.io/uploads/images/gallery/2023-12/image-1702383120826-56-18-am.png)
You can also verify the CNAME DNS record using the command line
1. On Mac or Linux, using the `terminal`
```bash
$ dig chat.element.io CNAME
; <<>> DiG 9.10.6 <<>> chat.element.io CNAME
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 57888
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 512
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;chat.element.io. IN CNAME
;; ANSWER SECTION:
chat.element.io. 299 IN CNAME element.element.io.
;; Query time: 32 msec
;; SERVER: 1.1.1.1#53(1.1.1.1)
;; WHEN: Fri Jul 31 10:21:56 BST 2020
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 91
```
2. On Windows, using `PowerShell`
```powershell
PS C:\Users\twilight> Resolve-DnsName -Name chat.element.io -Type CNAME
Name Type TTL Section NameHost
---- ---- --- ------- --------
chat.element.io CNAME 299 Answer element.element.io
```
11. Continue from step 11 on [Get Your Own EMS Server](get-your-own-ems-server)
## Provider-specific instructions
### GitHub Pages
If you are hosting your website with GitHub Pages, add this to the Jekyll config file `_config.yml`
```yaml
include:
- .well-known
```
### Microsoft Azure
If you are using Microsoft 365 / Azure to manage your domain or the rest of your infrastructure, please use the following instructions to host the `.well-known/matrix` URI (RFC 8615).
In this section, we will configure Azure to serve `https://yourdomain.com/.well-known/matrix/client` and `https://yourdomain.com/.well-known/matrix/client`.
The summary of steps is as follows:
- prepare json files
- create a Storage account then enable a Static website
- upload the json files to .well-known/matrix/ in the `$web` container
- create a CDN and an endpoint for this container
- create a `CNAME` DNS entry for your custom domain, pointing to your CDN endpoint
- associate your custom domain to your CDN endpoint
#### Prepare client and server .well-known files locally
On your computer, prepare two plain text files called `client` and `server` (again, notice the lack of file extension such as ".txt") which contain the following:
##### client
```json
{
"m.homeserver": {
"base_url": "https://your-tenant.ems.host"
},
"m.identity_server": {
"base_url": "https://vector.im"
},
"org.matrix.msc4143.rtc_foci": [
{
"type": "livekit",
"livekit_service_url": "https://jwt.call.your-tenant.io"
}
]
}
```
Remember to replace `your-tenant` by the name of your EMS tenant.
##### server
```json
{
"m.homeserver": {
"base_url": "https://your-tenant.ems.host:443"
}
}
```
Remember to replace `your-tenant` by the name of your EMS tenant.
You will be uploading these shortly.
#### Create a Storage account and Static website
##### Storage account
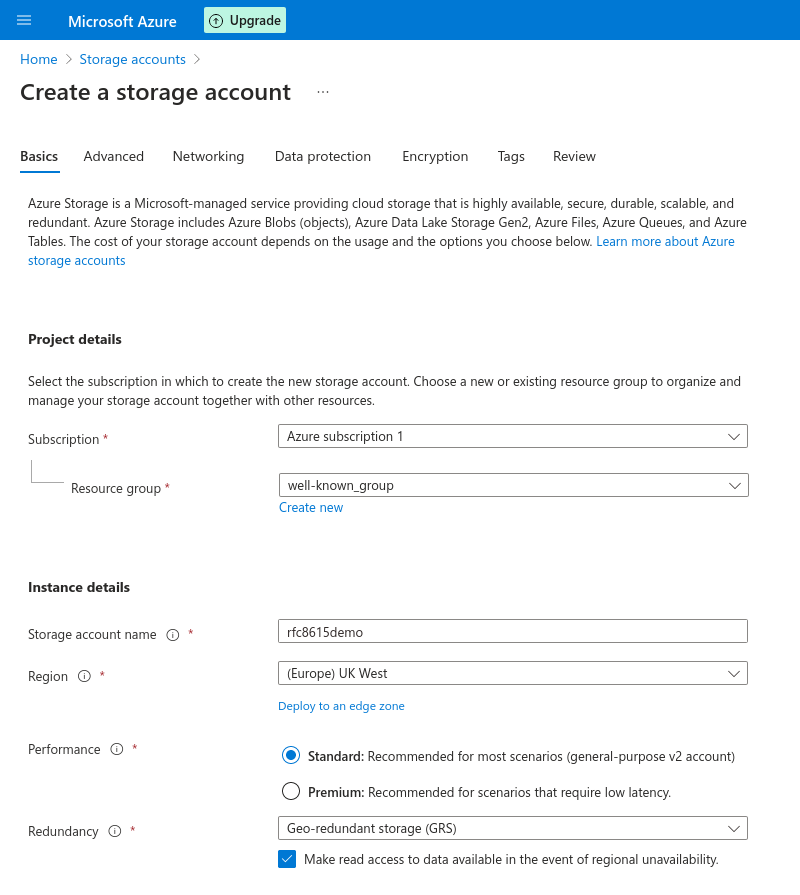
In the Azure Portal, [create a Storage account](https://portal.azure.com/#create/Microsoft.StorageAccount-ARM).
[](https://ems-docs.element.io/uploads/images/gallery/2023-11/screenshot-2023-11-10-at-14-20-46-microsoft-azure.png)
The name needs to be unique to Azure. `yourdomainwellknown` is an option that should work well in most scenarios.
Performarce can be left to Standard.
Redundancy should be set to Geo-redundant storage (GRS) as the .well-known URI will be a core part of your EMS deployment.
You can leave all other options to their default or change them to fit your specific deployment scenario.
Finally, click create.
##### Static website
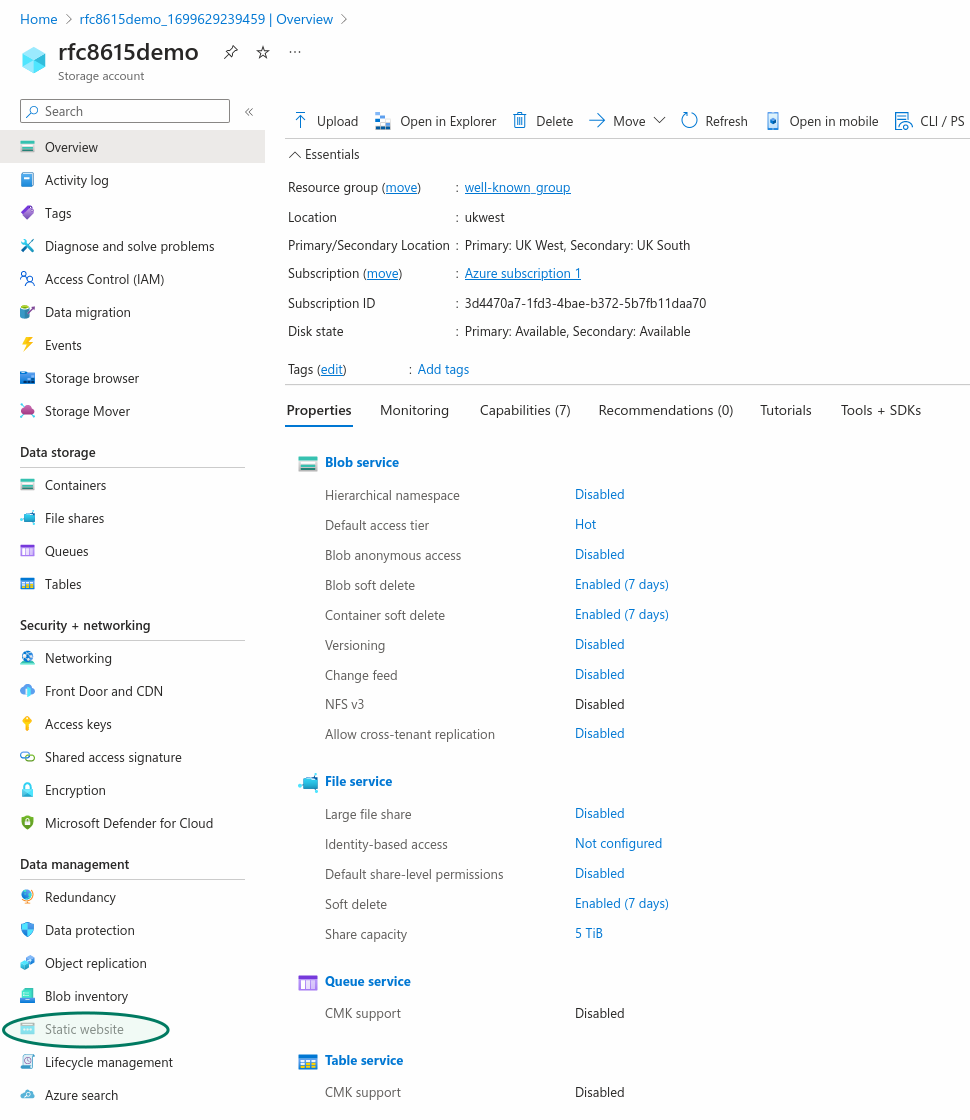
Once the Storage account is created, you will need to create a Static website in this Storage account.
In the Storage account overview, choose "Static website", in the Data management section.
[](https://ems-docs.element.io/uploads/images/gallery/2023-11/H3rscreenshot-2023-11-10-at-15-15-32-microsoft-azure.png)
You do not need to provide a specific Index document name or Error document path.
Enabling the Static website in your Storage account will automatically create a `$web` storage container to which you can upload the json text files which will be served at the .well-known URI.
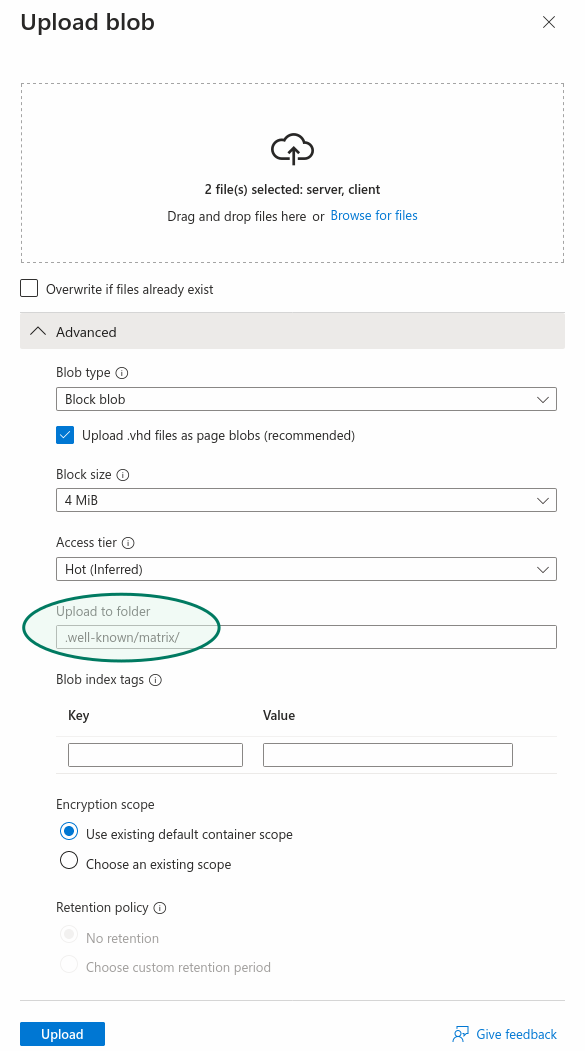
Go to "Containers", in the "Data storage" section, to upload the `client` and `server` files you prepered earlier.
Click on the `$web` container, then chose "Upload", which will open a panel on the right.
When uploading the `client` and `server` files, make sure to open the "advanced" part of the upload panel and choose to upload to a specific folder: `.well-known/matrix/`
[](https://ems-docs.element.io/uploads/images/gallery/2023-11/screenshot-2023-11-10-at-15-47-44-microsoft-azure.png)
#### Create a CDN, `CNAME` DNS entry for your custom domain and Custom domain name for the CDN endpoint
Creating a CDN is needed because Azure does not allow serving HTTPS over a custom domain using only a Storage account Static website. To do so, a CDN is necessary.
##### Create a CDN endpoint
Go back to your Storage account's main view and choose "Front Door and CDN" in the Security + Networking section, to create a CDN endpoint.
[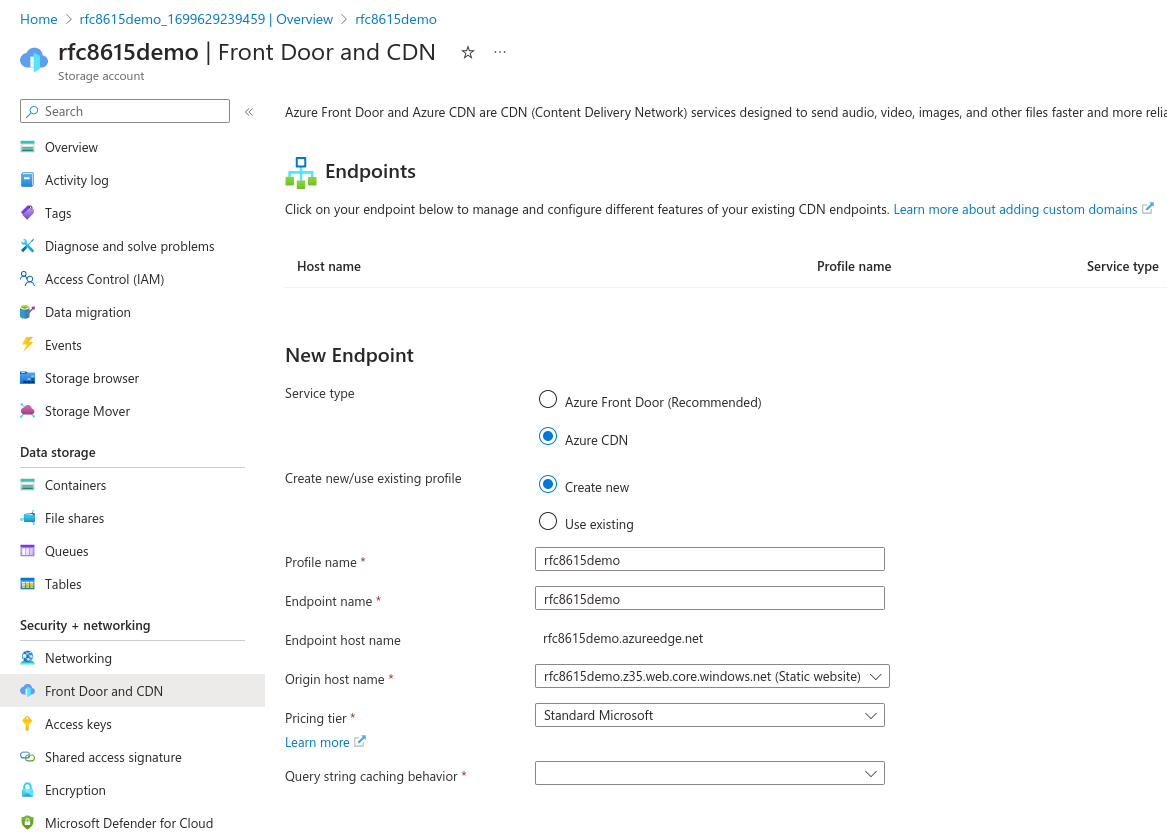](https://ems-docs.element.io/uploads/images/gallery/2023-11/screenshot-2023-11-10-at-15-57-51-microsoft-azure.png)
Service type: Azure CDN is sufficient, the more advanced features of Azure Front Door are not necessary here.
If you need to create a new profile, you may call the Profile name and Endpoint name as you wish.
For consistency, it is suggested to call them `yourdomainwellknown` as previously.
For Origin host name, pick your Static website.
For Query string caching behaviour, pick Ignore Query String, although this setting is not important in our context.
Once your endpoint is deployed, go to the resource, then go to your endpoint's further settings by clicking on it. Make note of its hostname (`rfc8615demo.azureedge.net` in our example) as you will need it shortly.
[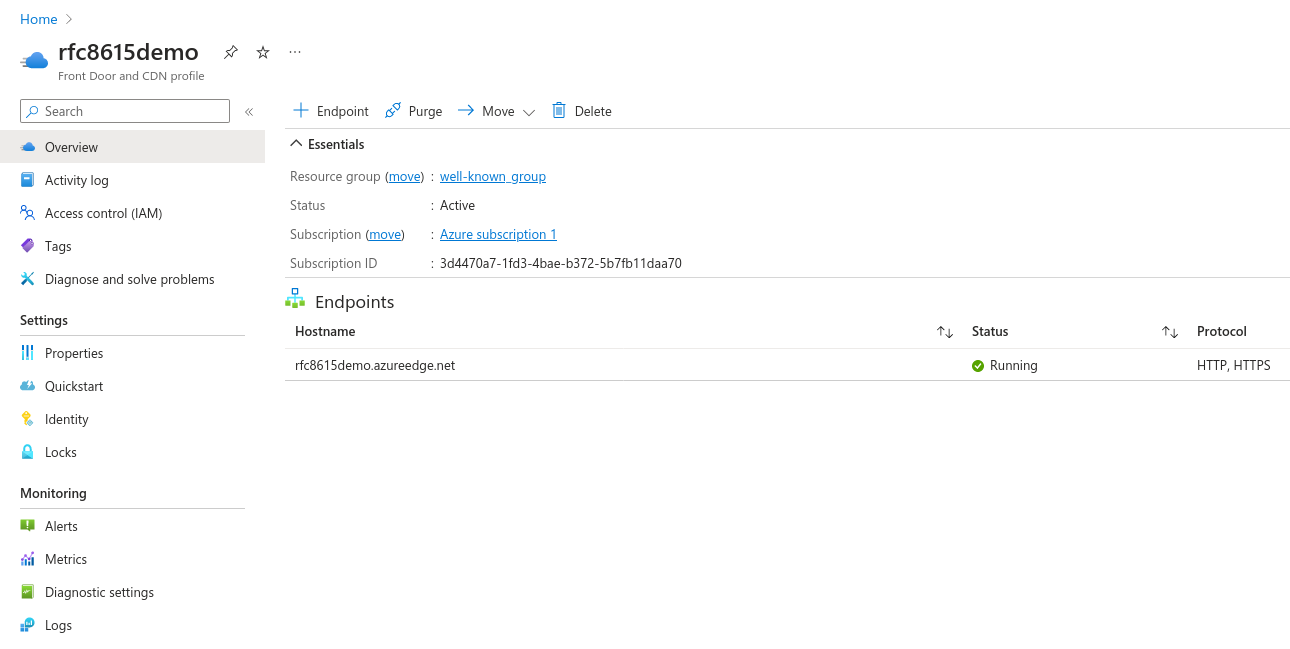](https://ems-docs.element.io/uploads/images/gallery/2023-11/screenshot-2023-11-10-at-16-09-22-microsoft-azure.png)
##### Create `CNAME` DNS entry for your custom domain
You will now create a DNS entry for your custom domain, a `CNAME` pointing to your Azure CDN endpoint's hostname. How to do so exactly will depend on who hosts your DNS servers. The specifics of this are beyond this documentation, but the following general information should be sufficient.
In your DNS provider's admin panel, add a DNS entry with the following details:
- Type: `CNAME`
- Domain: your custom domain, such as `yourdomain.com`
- Target: your Azure CDN Endpoint's hostname, such as `rfc8615demo.azureedge.net` in our example
Once created, this DNS entry may take some time to propagate, but in most cases will be picked up quickly by Azure, as needed in the next step.
##### Associate your custom domain with your CDN Endpoint
In the endpoint's settings, choose "+ custom domain" to start adding your custom domain. A panel will open on the right.
Enter your custom domain: `yourdomain.com` and finally, click add.
If the `CNAME` entry can be seen by Azure, after a few minutes your custom domain should be associated with your CDN Endpoint.
#### Final result
`https://yourdomain.com/.well-known/matrix/client` and `https://yourdomain.com/.well-known/matrix/server` are now served over HTTPS by Azure.
You should now have the following resources in your Azure account:
- Storage account
- Front Door and CDN Profile
- Endpoint
#### Resources
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cdn/cdn-create-a-storage-account-with-cdn
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cdn/cdn-storage-custom-domain-https